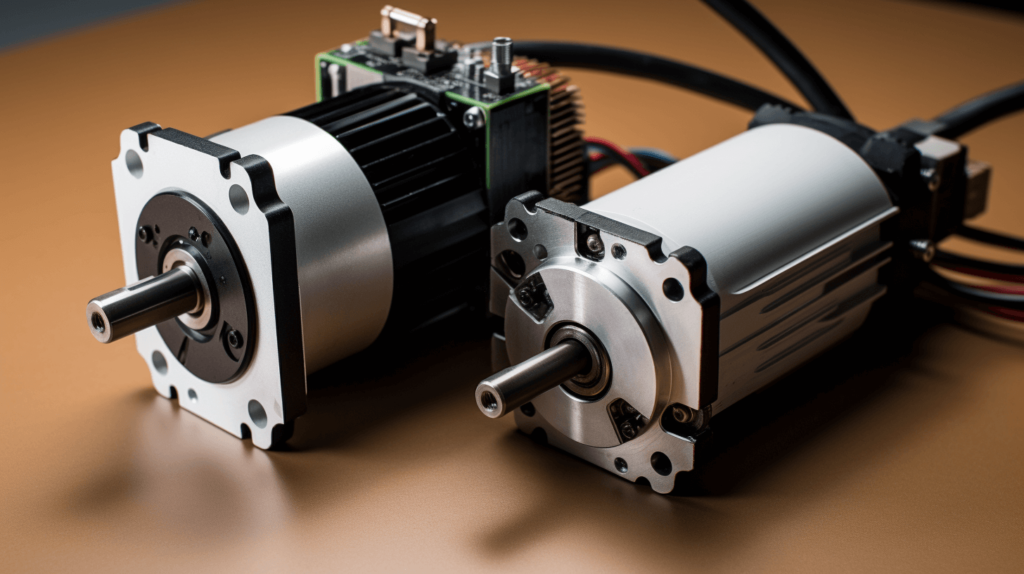
Stepper and servo motors are both commonly used in automation and robotics applications. But what are the key differences between these two motor types and how do you determine which is best for your specific project? This guide will compare stepper and servo motor construction, functionality, pros and cons, costs, and ideal use cases.
Stepper Motor Basics
Stepper motors operate by converting electrical pulses into discrete mechanical movements or steps. Key features:
- Constructed with a permanent magnet rotor and wound stator.
- Driven by direct current, which energizes the stator coils to magnetically rotate the rotor in steps.
- Open loop control, so no feedback required.
- Excellent low speed torque and precision, due to high pole count.
- Holds position when at rest.
- Drawbacks include torque reduction at high speeds and inability to react to load changes.
Overall, steppers excel in applications requiring high precision and holding torque at low speeds. They’re simple to control and provide a cost-effective solution.
Servo Motor Basics
Servo motors use position feedback for closed loop speed and torque control. Key features:
- Constructed with a 3-phase stator and permanent magnet rotor.
- Driven by alternating current, which rotates the magnetic field to turn the rotor.
- Closed loop control requires position feedback.
- Maintains consistent torque across speed range.
- Precisely controllable speed, position, and torque.
- Drawbacks include higher costs and complexity.
Servos are ideal for applications needing high speeds, dynamic movements, and torque adjustment. Their precision control enables complex motion profiles.
Choosing Between Stepper and Servo
- Consider torque requirements at target speeds.
- Stepper best for low speed, high precision needs. Servo best for high speeds while maintaining torque.
- Servo recommended for changing loads, stepper better for constant loads.
- Stepper provides holding torque at zero speed, servo requires braking.
- Servo enables force control, stepper does not.
- Servo more expensive, stepper simpler and more cost effective.
By understanding these key differences, you can determine whether a stepper or servo motor is best suited for your automation application needs.