How Do Electric Motors Work? A Complete Explanation

Electric motors are essential devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. But how exactly do electric motors work to spin motors and generate torque?
Key Considerations for Selecting Brushless DC Motor Bearings

Brushless DC (BLDC) motor bearings, also known as electric motor bearings or motor bearings, are specialized bearings designed specifically for use in electric motors and drives. Bearings support and guide the motor shaft while allowing it to rotate smoothly
Unlocking the Power of Brushless DC Gear Motors
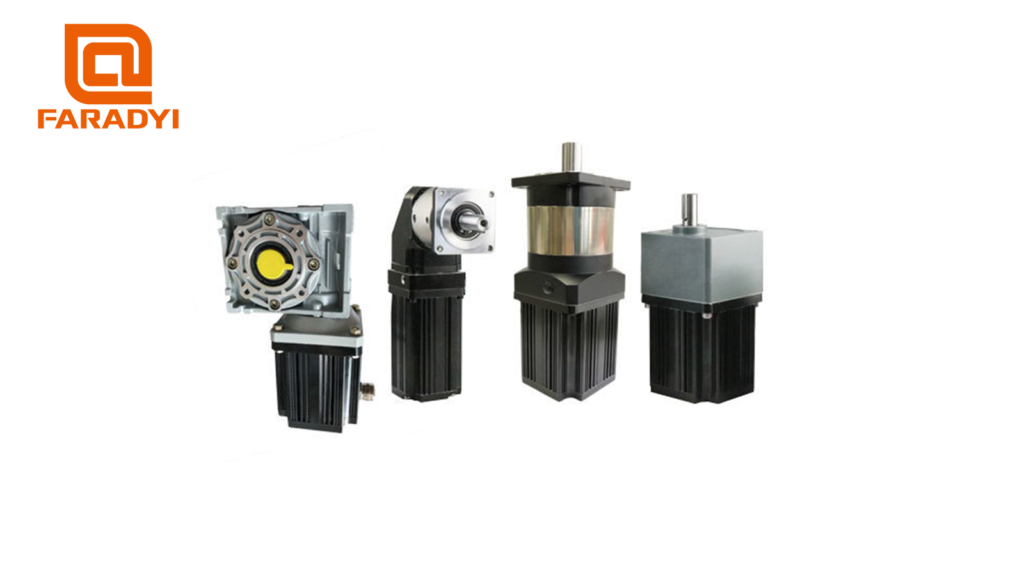

In the realm of automation, the integration of brushless DC gear motors has revolutionized industries, providing a seamless combination of efficiency and versatility. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of how brushless DC gear motors achieve speed reduction
Causes of Vibration and Noise in Stepper Motors and Their Solutions

When driving a stepper motor, if you notice significant noise emanating from within the motor when it’s in a stationary state, resembling rapid changes in coil activity, it is often due to the motor operating in an oscillation zone.
Benefits of 3-Stage Planetary Gearboxes: Higher Ratios, Torque, and More
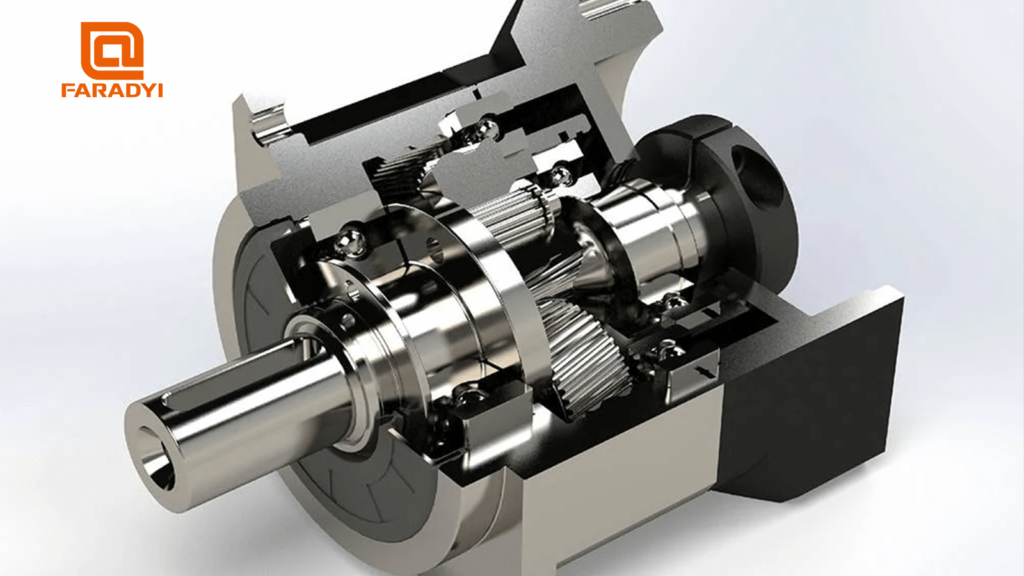
A 3-stage planetary gearbox has three sets of planetary gears inside, providing greater reduction ratios, output torque, efficiency, and precision compared to single or 2-stage gearboxes.
Causes and Preventive Measures for Demagnetization in Permanent Magnet Brushless Motors
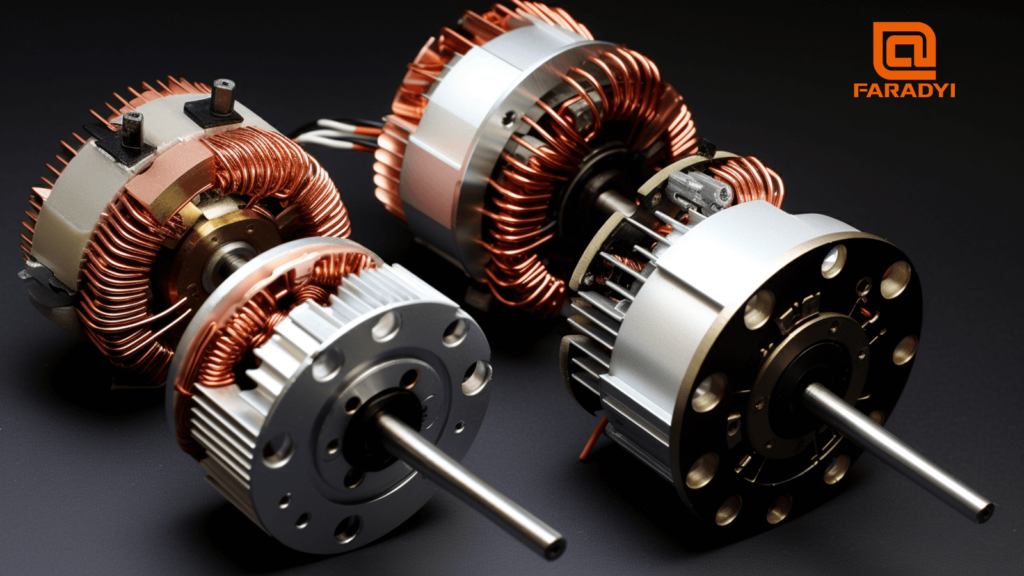

During the operation of permanent magnet brushless motors, the most significant risk is demagnetization caused by high temperatures. It is widely known that the crucial component of permanent magnet brushless motors is the magnetic steel
How to Control the Speed of a DC Motor: Best Methods
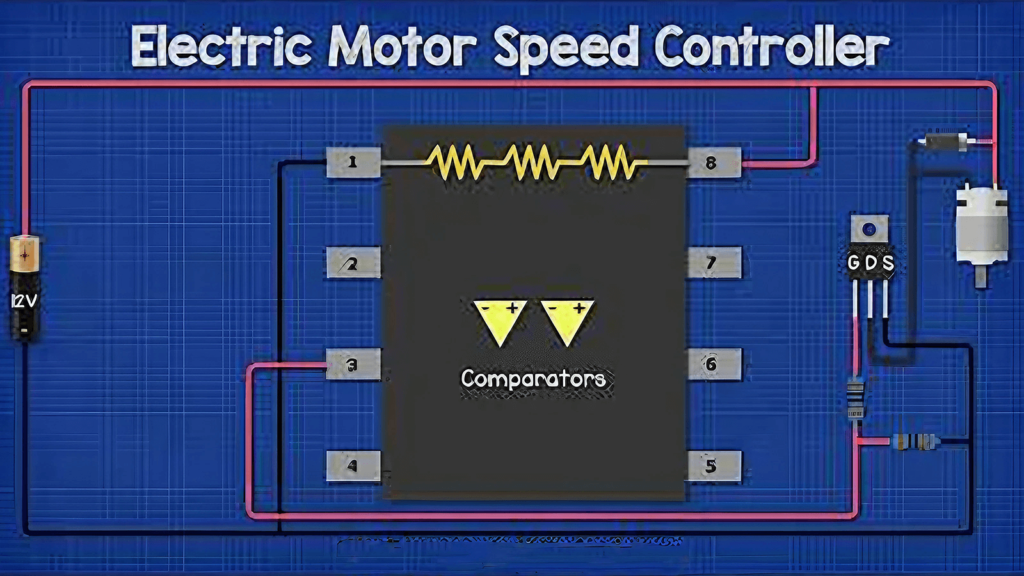
DC motors are electric motors that run on direct current power. Controlling the speed of a DC motor is essential in many applications to vary motor speed according to requirements and optimize functionality. Speed control allows regulating the movement of motors in devices like vehicles, elevators, and more.
Causes and Preventive Measures for Demagnetization in Permanent Magnet Brushless Motors
In the usage of permanent magnet brushless motors, the most significant risk is demagnetization caused by high temperatures. It is well-known that the critical component of permanent magnet brushless motors is the magnetic steel, and magnetic steel is highly susceptible to temperature.
Analysis of the Formula for Calculating Commutation Noise Frequency in Brushless Motors

This article provides a brief analysis of the formula for calculating commutation noise frequency in brushless motors. Brushless motors operate in six different states, denoted by 1 and 0, representing the direction of current flow in the three-phase winding—1 for positive and 0 for negative. Positive current flows from the first end to the last end of the winding, while negative current flows from the last end to the first end.
Reasons and Solutions for Overheating of Brushless Motor Bearings

This article provides a comprehensive introduction to brushless motor bearings, focusing on the reasons behind overheating and effective solutions.
I. Understanding Bearing Overheating
In general terms, bearing overheating refers to a temperature exceeding 95°C for rolling bearings and 80°C for sliding bearings.
