What You Should Know About Frameless Motors

Before discussing frameless motors, let’s first take a look at the components that go into them. A frameless motor consists of a stator assembly and rotor assembly with permanent magnets. Hall effects may be offered ..
How To Choose Motors For Robot ?

Selecting the right motors for a collaborative robot dedicated to research and education is indeed crucial for achieving precise and efficient movements. Here are some key criteria to consider when choosing motors for such a robot
Planetary Gearmotors: A Complete Guide to Their Operation and Benefits
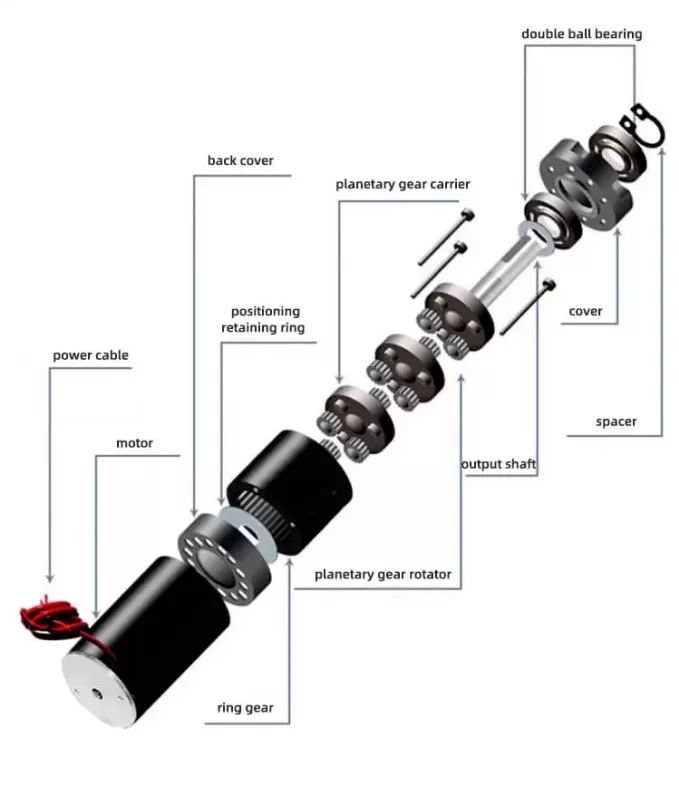
Planetary gearmotors are an extremely useful type of compact, high-precision gearbox used across various industries to achieve precise motion control. This in-depth…
Understanding Worm Gear Motors: A Complete Guide
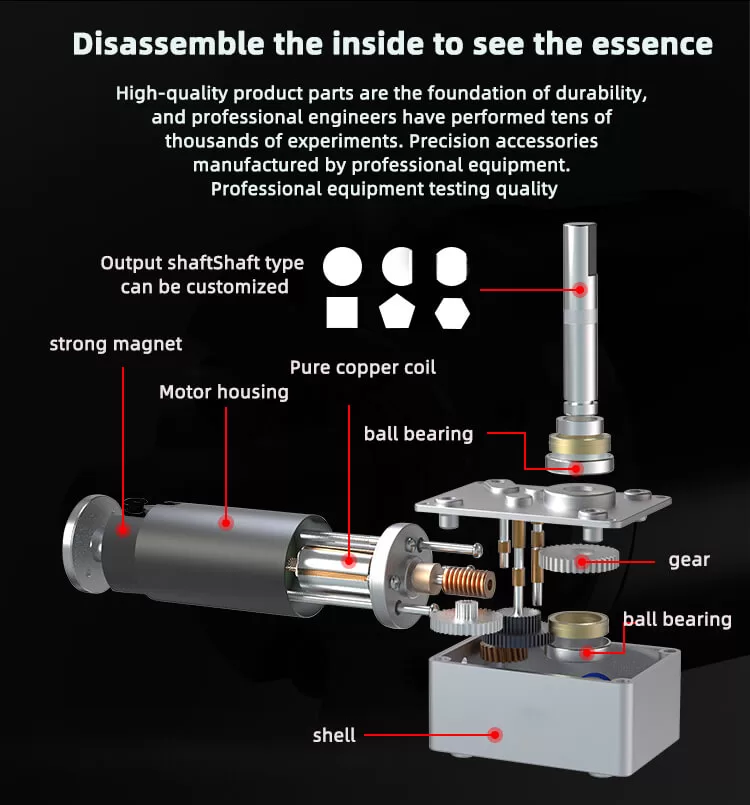
Worm gear motors are a unique type of motor valued for their compact size, high torque, and quiet operation. Here is a complete guide to understanding how worm gear motors work and their key advantages.
What Is Gear Motor and How Do They Work?

A gear motor is a type of electric motor that uses a gear reduction system to increase torque while reducing speed. Gear motors combine the power of an electric motor with the torque multiplying capacity of a gear reducer in a single compact package. A gear motor consists of an electric motor directly connected to […]
How Does a Brushless DC Motor Work?
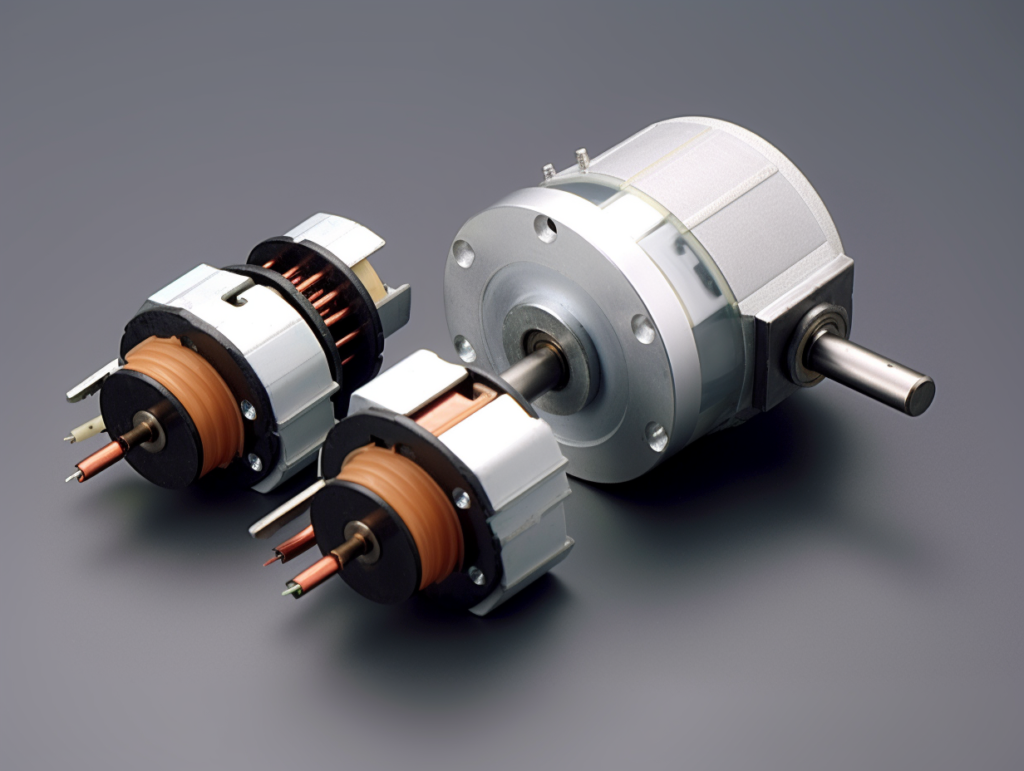

Brushless DC (BLDC) motors are growing in popularity due to their high efficiency, low maintenance requirements, and controllable speed. But how do these electronically commutated motors work without brushes…
How To Choosen The Appropriate Drive Motors for Autonomous Vehicles
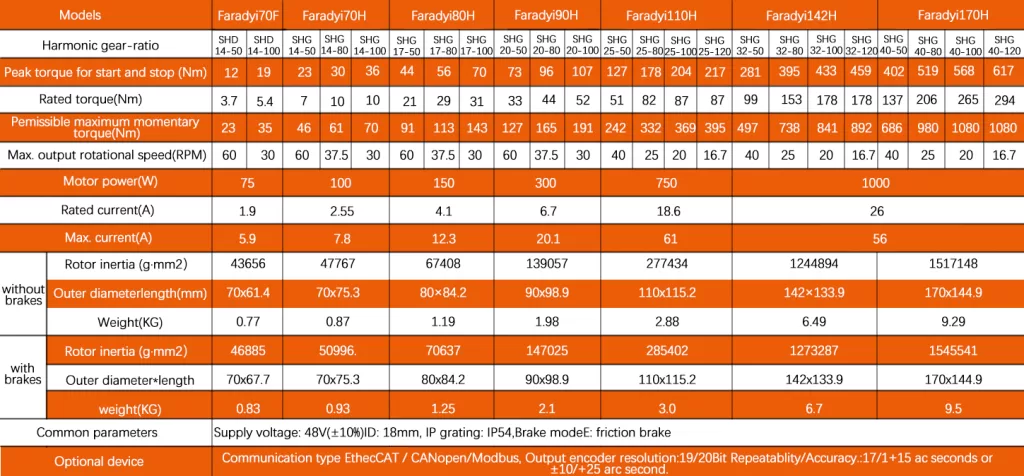
Transitioning from Hollywood’s depiction of automated machines, from characters like Bruce Dern in Silent Running, Arnold Schwarzenegger in the Terminator series…
What Is A Brushless DC Motor
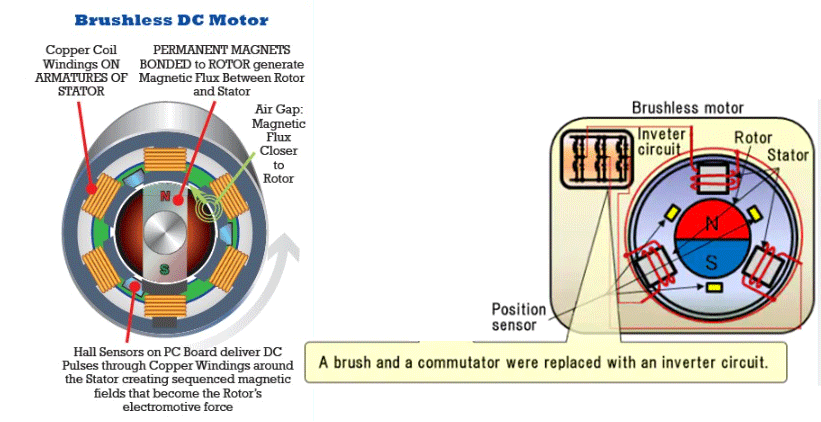
A brushless DC (BLDC) motor is a type of electric motor that utilizes electronic commutation instead of mechanical brushes and commutators to power the rotor. BLDC motors rely on internal position sensors and external electronic controllers to energize the stator windings in a specific sequence to create rotational motion.
