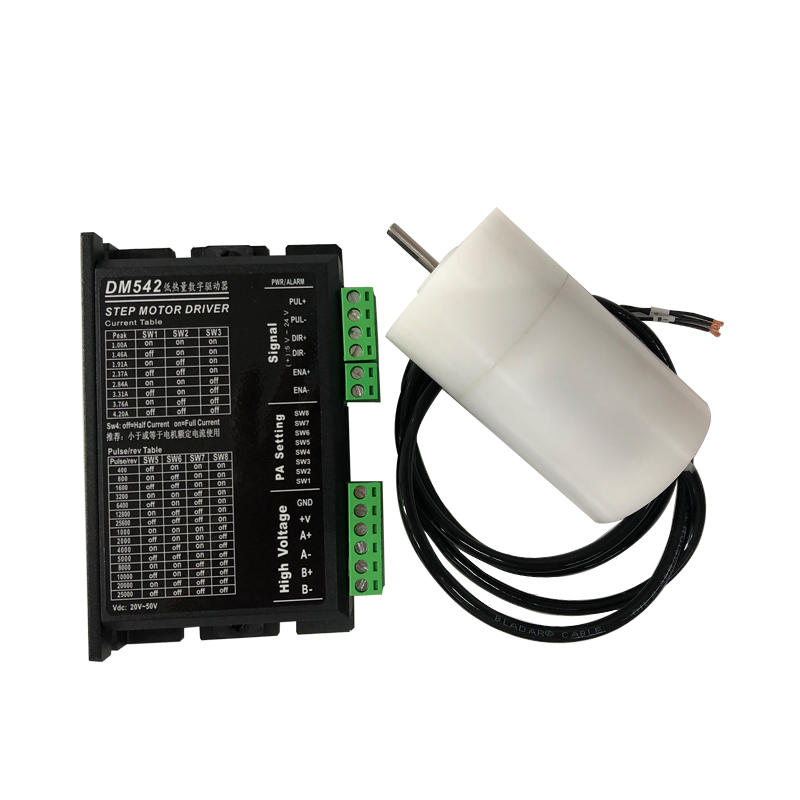
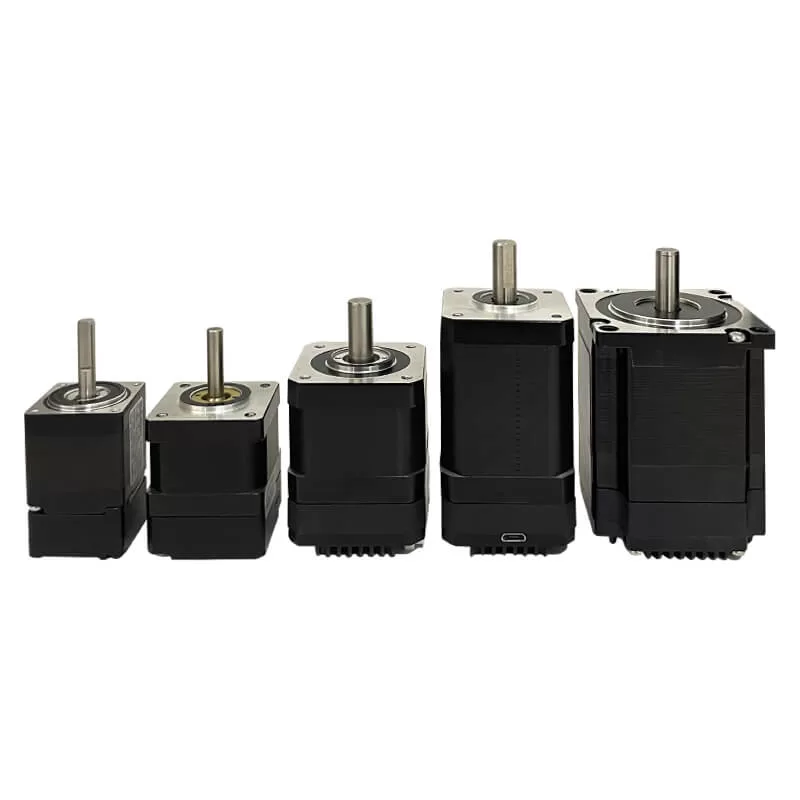
When selecting a stepper motor, it’s crucial to consider the advantages and disadvantages of various motor types. Let’s explore the pros and cons of stepper motors with different phase numbers:
Two-Phase Permanent Magnet (PM) Stepper Motors
Pros:
- Cost-Effective: Generally, the price is half that of the equivalent size Hybrid (HB) stepper motors.
- Lower Noise: Due to a larger air gap, claw-pole construction, and a larger step angle, there are fewer transitions at the same speed, resulting in lower noise.
Cons:
- Lower Resolution: The low resolution (larger step angle of 7.5°) leads to poorer position accuracy compared to Hybrid (HB) stepper motors.
- Torque Fluctuation: Large torque fluctuations, especially at low speeds (below 200 rpm).
- Magnetic Saturation: The larger air gap may cause magnetic saturation at the root of the claw pole, resulting in reduced output torque.
- Short Lifespan: Metal sliding bearings with a short lifespan.
- Temperature Sensitivity: The rotor, typically made of ferrite magnets, exhibits poor temperature characteristics, leading to a greater torque decrease over extended use.
Two-Phase Hybrid (HB) Stepper Motors
Pros:
- High Resolution: Widely used due to higher resolution (commonly 1.8° step angle).
- High Torque: Offers substantial torque.
- Cost-Efficient: More economical compared to multi-phase HB stepper motors.
Cons:
- Vibration at Low Speeds: Pronounced vibration at very low speeds, with resonance around 60 rpm.
- High-Speed Noise: Generates significant noise at high speeds.
- Torque Fluctuation at Half-Step: Larger torque fluctuation (1:1.14) during half-stepping.
- High Coil Impedance: Higher coil impedance results in lower torque at high speeds.
Three-Phase Hybrid (HB) Stepper Motors
Pros:
- Higher Resolution: 1.5 times the resolution of two-phase motors, enabling high-precision positioning.
- Higher Torque Efficiency: Better torque efficiency with a main pole number of 6 in the stator.
- Reduced Vibration: Three-phase structure minimizes vibration compared to two-phase motors.
- Reduced Cogging Torque: Cogging torque is reduced compared to two-phase motors.
Cons:
If designed with 12 main poles, the structure can be more complex than the eight main pole structure of two-phase motors.
Three-Phase Permanent Magnet (PM) Stepper Motors
Pros:
- Higher Resolution: Over 1.5 times the resolution of two-phase PM stepper motors.
- Lower Vibration and Noise: Reduced vibration and noise compared to two-phase PM or two-phase HB stepper motors.
- Higher High-Speed Torque: Greater torque at high speeds compared to two-phase PM stepper motors.
- Cost-Effective: More affordable than HB stepper motors.
- Efficient Drive: Requires only six power transistors for driving.
Cons:
More structurally complex than two-phase PM stepper motors.
In conclusion, choosing the right type of stepper motor is crucial to avoid potential issues. Consider factors such as the required output torque, step angle, and optimal drive method to make an informed decision for your application.