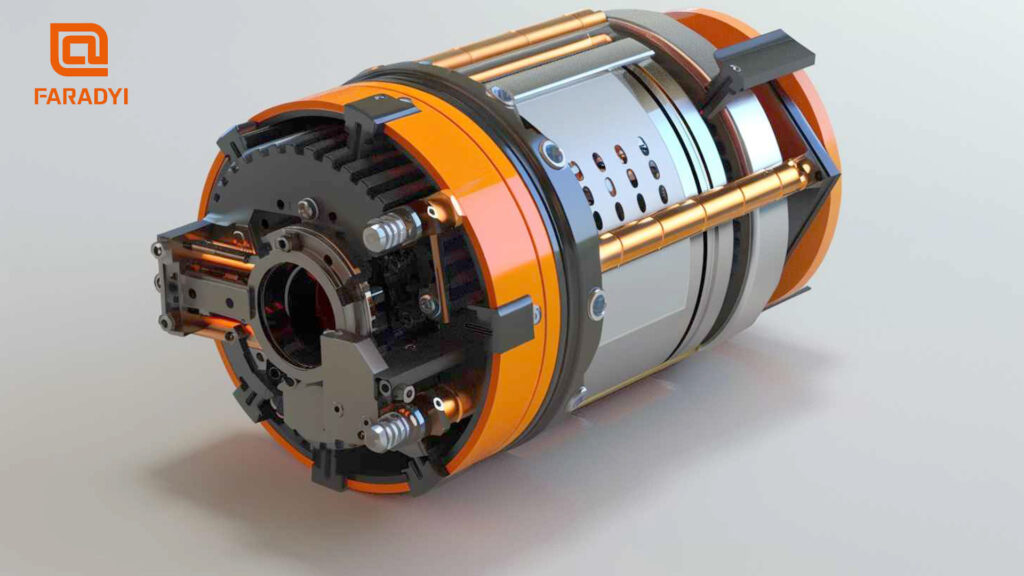
Principles of Brushless DC Gear Motors
A brushless DC gear motor refers to the integration of a gearbox and a brushless DC motor, typical of electromechanical integration. Brushless DC gear motors use electronic commutation devices to replace traditional mechanical commutation devices (commutators and brushes), retaining the excellent speed regulation and starting characteristics of DC motors while also offering the advantages of a simple structure and easy maintenance similar to AC motors. These motors have good performance, reliable operation, simple maintenance, and long lifespan, leading to rapid development in recent years. Unlike traditional DC motors where the armature rotates and the magnetic poles are stationary, brushless DC motors are the opposite, with rotating magnetic poles and a stationary armature. The commutation of the armature winding current can be achieved using position sensors and electronic switch circuits.
Model Selection of Brushless DC Gear Motors
Generally, choose an appropriate power based on actual requirements, then select the suitable torque, power, and speed ratio. The driver is used for speed control, providing adjustable speeds within a range. In contrast, a gear motor can only have one speed output. The speed ratio of the gear motor is selected based on the required actual speed and the actual speed of the motor.
Connection Methods of Brushless DC Gear Motors
Brushless DC motors have 3 winding leads and 5 Hall sensor leads. These 8 leads must correspond one-to-one with the corresponding leads of the driver; otherwise, the motor cannot operate normally.
In general, for brushless DC motors with 60-degree and 120-degree phase angles, they need to be driven by brushless drivers with corresponding 60-degree and 120-degree phase angles, which cannot be directly interchanged. For a 60-degree brushless DC motor, there are two correct wiring methods for the 8 leads connected to the 60-degree brushless driver, one for forward rotation and one for reverse rotation.
For 120-degree brushless DC motors, by adjusting the phase sequence of the coil leads and the Hall sensor leads, there are 6 correct wiring methods for the 8 leads connected to the brushless driver, with 3 for forward rotation and 3 for reverse rotation.
If the brushless DC motor rotates in the wrong direction, it indicates that the phase angle of the brushless driver is not matched with the brushless DC motor. To adjust the motor direction, interchange the Hall sensor leads A and C of the brushless DC motor with the brushless driver, and simultaneously interchange the main phase leads A and B of the brushless DC motor with the brushless driver.
Contact Us
Faradyi Technology Co., Ltd is an innovation-centric enterprise with integrated R&D, production, and sales of brushless DC motors, DC brush motors, DC gear motors, waterproof motors, and related accessories. The company excels in OEM/ODM with thorough and satisfactory service. Our products are popular and well received in both domestic and foreign markets, including Europe, America, Asia, Africa, Australia, the Middle East, and other regions. The company adheres to its business philosophy of “Quality, continuous improvement, excellence, innovation” for its products and “integrity, practicality, timeliness, efficiency” for its services.