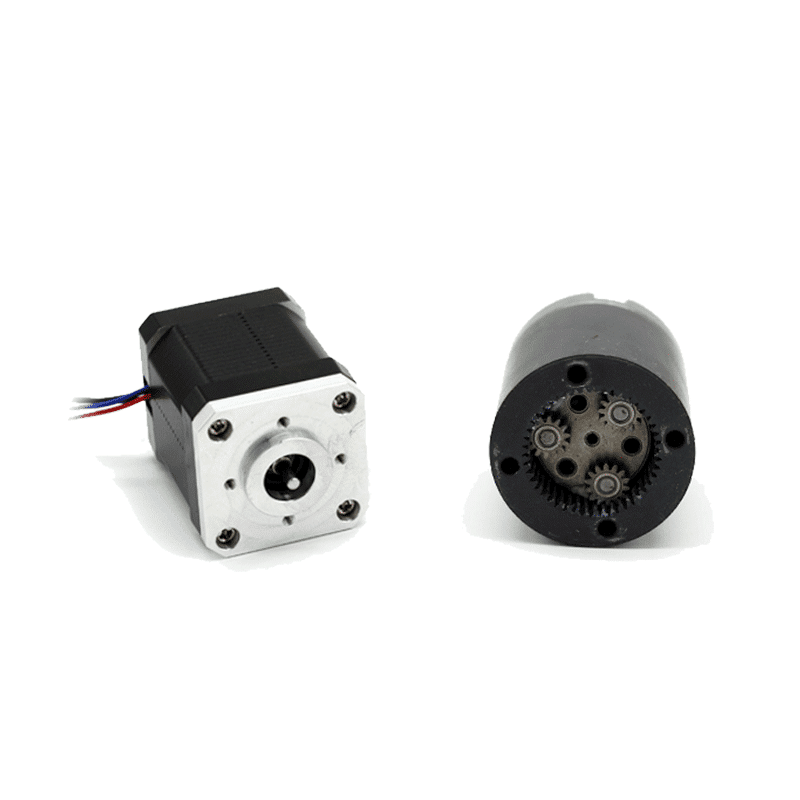
The two-phase four-wire stepper motor, as a digital actuator, has found widespread applications in motion control systems. Many users may experience significant heating when using the two-phase four-wire stepper motor, causing concerns about the normality of this phenomenon. In reality, heating is a common occurrence in two-phase four-wire stepper motors, but severe overheating can impact motor performance and is considered abnormal. Here are some ways to minimize overheating in two-phase four-wire stepper motors:
-
Reduce Copper and Iron Losses:
To decrease heating in two-phase four-wire stepper motors, efforts should be made to reduce copper and iron losses. Reducing copper losses involves two main directions: decreasing current and resistance. This requires selecting motors with lower rated current and resistance whenever possible. For two-phase four-wire stepper motors, using series-connected motors instead of parallel-connected motors can help reduce copper losses, although this may conflict with torque and high-speed requirements. -
Utilize Driver Functions:
For selected motors, it’s crucial to leverage the functions of the driver to minimize overheating. The driver’s offline function and automatic half-current control function are particularly useful. The automatic half-current control function automatically reduces the current when the motor is static, while the offline function completely cuts off the current. -
Consider Microstepping Drivers:
Additionally, microstepping drivers, which produce a current waveform closer to sine waves with fewer harmonics, can help reduce harmonic losses and, consequently, motor heating. These drivers provide smoother operation and less heat generation. -
Select Appropriate Voltage Level:
Choose an appropriate drive motor voltage level that balances high-speed performance, smoothness, and heating, considering that high-voltage drive motors may enhance high-speed characteristics but also increase heating.
In summary
For various two-phase four-wire stepper motors, both copper and iron losses contribute to heating. Copper losses result from resistance and current, while iron losses are associated with the voltage level, material, current, frequency, and voltage. The two-phase four-wire stepper motor generally pursues positioning accuracy and torque output, leading to lower efficiency, higher current, and significant harmonic components, contributing to noticeable heating compared to typical AC motors. By implementing the suggested solutions, users can work towards minimizing overheating and optimizing the performance of two-phase four-wire stepper motors.