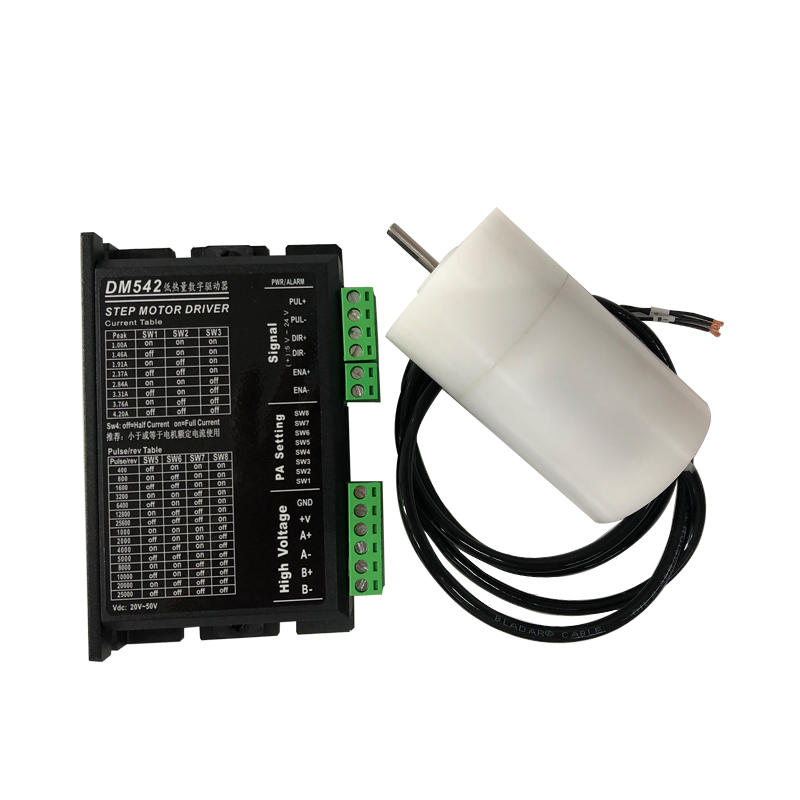
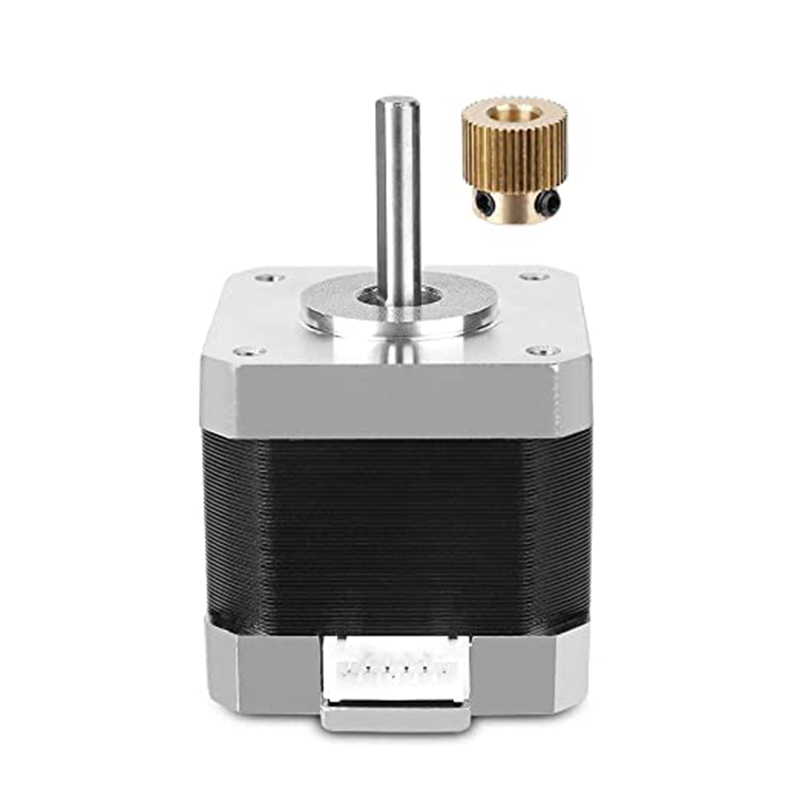
Hybrid stepper motors are a popular type of stepper motor used in many applications requiring precise positioning and rotation. They combine features from both variable reluctance and permanent magnet stepper motors to provide better performance.
What is a Hybrid Stepper Motor?
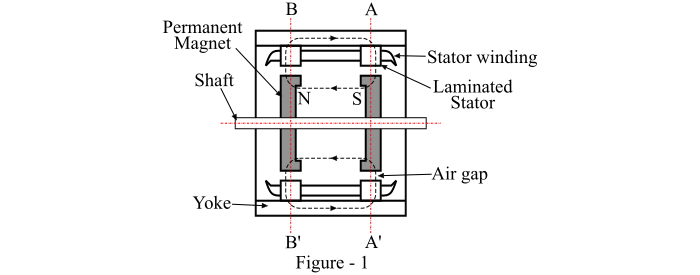
A hybrid stepper motor has a rotor with permanent magnets and laminated steel teeth. The stator has wound wire coils around laminated steel poles. The rotor’s permanent magnets are magnetized axially, with the poles labeled north and south.
The teeth on the rotor’s end caps are offset by half a tooth pitch. This gives the motor a defined step angle, usually 1.8 or 0.9 degrees. The offset teeth interact with the rotating magnetic fields from the stator coils to cause rotational movement.
How Do Hybrid Stepper Motors Work?
When current flows through the stator coils, it magnetizes the poles. This attracts the rotor’s teeth into alignment. When current direction reverses, the rotor turns slightly to align in the new orientation.
By sequencing current through the phases of coils, the rotor turns in incremental steps. Exciting the phases in the order +A, +B, -A, -B rotates the motor counter-clockwise. Reversing to +A, -B, +B, +A rotates it clockwise.
Key Benefits of Hybrid Stepper Motors
- Precise positioning and control – steps are repeatable and accurate
- Good holding torque when powered off due to permanent magnets
- High torque relative to size
- Low tendency to resonate compared to variable reluctance motors
Drawbacks of Hybrid Stepper Motors
- More expensive than variable reluctance motors
- Performance varies with temperature due to magnets
- Higher inertia due to permanent magnets
In summary, hybrid stepper motors combine the best features of different designs for optimal precision and performance. Their incremental rotational movement and holding torque make them ideal for applications like 3D printers, CNC machines, and more.