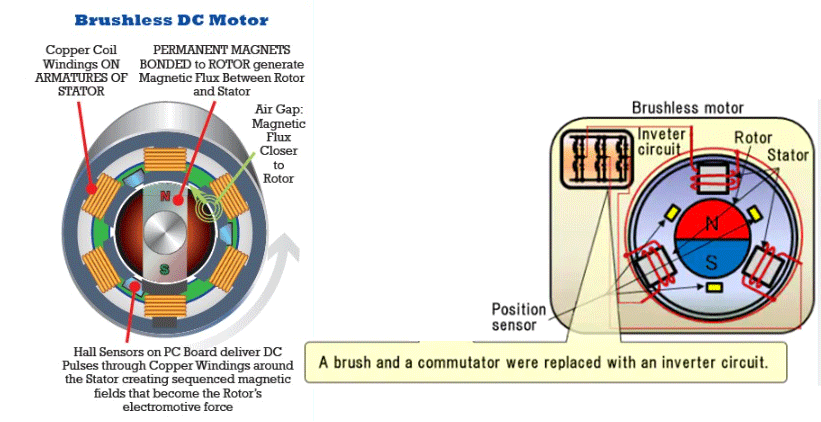
A brushless DC (BLDC) motor is a type of electric motor that utilizes electronic commutation instead of mechanical brushes and commutators to power the rotor. BLDC motors rely on internal position sensors and external electronic controllers to energize the stator windings in a specific sequence to create rotational motion.
How Brushless DC Motors Work
Brushless DC motors have two main components:
- A stator containing multiple windings, usually three, spaced evenly around the motor.
- A rotor containing permanent magnets that generate a constant magnetic field.
The key lies in the electronic controller, which monitors the rotor’s position and energizes the stator windings in a timed sequence. This creates a rotating magnetic field that interacts with the rotor’s magnetic field to generate torque.
As the rotor magnets are pushed and pulled by the rotating stator field, continuous rotation is produced. Speed and torque are precisely regulated by controlling the timing and sequencing of the stator windings.
Advantages of Brushless DC Motors
Some key advantages of brushless DC motors over brushed DC motors:
- Higher efficiency – no brush friction losses improves efficiency
- Increased lifespan – no brushes equals lower wear on components
- Precise speed and torque control – enabled by electronic commutation
- Compact size yet high power density
- Low maintenance requirements – no brushes to replace
- Smooth and quiet operation
- High reliability in harsh environments
Applications of Brushless DC Motors
Brushless DC motors are widely used in industries and devices such as:
-
Electric vehicles
-
Industrial automation
-
Robotics
-
Drones
-
Aerospace systems
-
Computer peripherals
-
HVAC systems
-
Home appliances
-
Medical equipment
In summary, the unique advantages of brushless DC motors make them ideal for applications requiring high efficiency, precision control, low maintenance, and reliability. Their working principle relies on electronic commutation to energize stator windings rather than mechanical brush contacts.