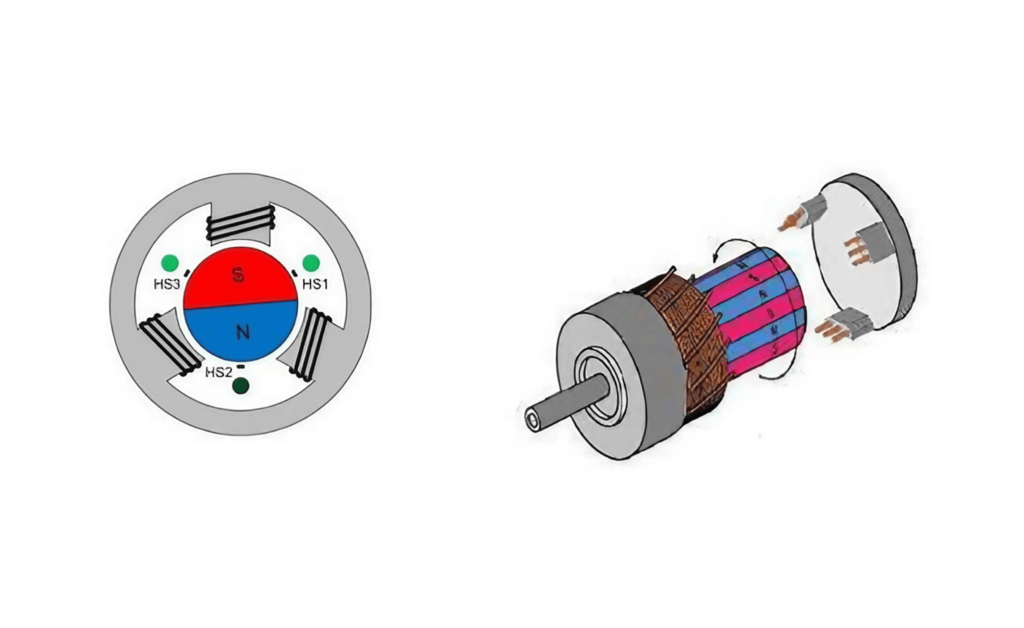
If you’re acquainted with using brushless motors, you’re likely familiar with the concept of position sensors. However, the precise role of these sensors might be less clear. In the realm of brushless motors, position sensors play a crucial role in measuring the rotor pole’s position, providing accurate commutation information to the logic switch circuit—essentially converting position data. This type of brushless motor is often referred to as “sensored” brushless motors. The sensors detect the alignment of the rotor magnetic poles, generating electrical signals that control the commutation of the stator winding.
There’s a variety of position sensors, each with its unique characteristics. Among the commonly used position sensors by brushless motor manufacturers, three stand out: electromagnetic position sensors, magnetic proximity sensors, and optoelectronic position sensors.
1. Electromagnetic Position Sensors in DC Brushless Motors:
In DC brushless motors, open-loop transformers find widespread application in electromagnetic position sensors. The open-loop transformer in a three-phase brushless motor consists of a stator and a tracking rotor. The stator typically features six magnetic poles with a 60-degree separation. One set of three poles forms a winding that connects to a high-frequency power source. The remaining three poles are wound separately with secondary windings wa, wb, and wc.
2. Magnetic Sensing Position Sensors:
Magnetic sensing position sensors are a type of semiconductor sensor whose electrical parameters change in response to variations in the surrounding magnetic field. This type of sensor operates on the principles of the Hall effect and magnetic resistance. Commonly used magnetic sensors include Hall elements or integrated circuits, magnetoresistive sensors, and magnetoresistive diodes.
3. Optoelectronic Position Sensors:
Optoelectronic position sensors are devices sensitive to the position of light spots on their photosensitive surfaces. These sensors operate based on the lateral photoelectric effect, offering not only precise positioning capabilities like photodiode arrays and CCD but also high sensitivity, resolution, fast response times, and simple circuit configurations.
Conclusion
Understanding the significance of these position sensors in brushless motors is crucial for optimizing their performance and ensuring precise control over various applications. Whether it’s the robustness of electromagnetic sensors, the versatility of magnetic sensors, or the advanced features of optoelectronic sensors, choosing the right sensor type is paramount for achieving optimal brushless motor functionality in diverse settings.