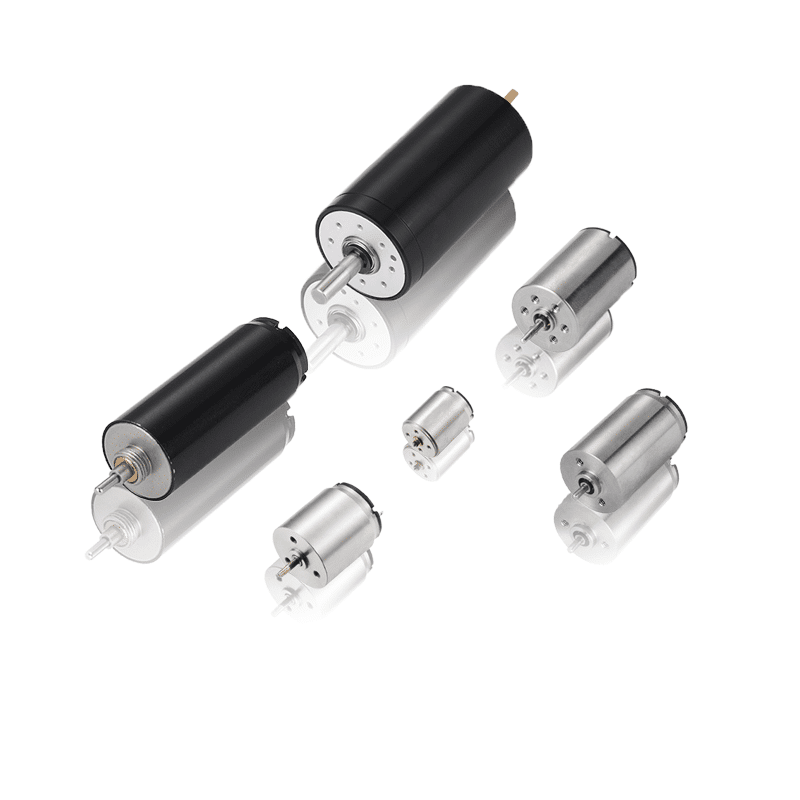
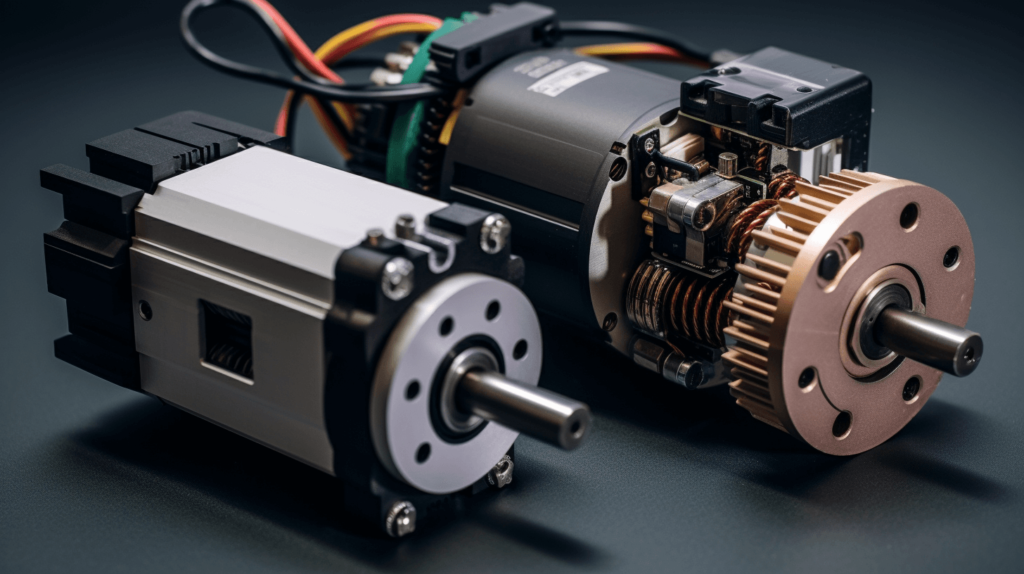
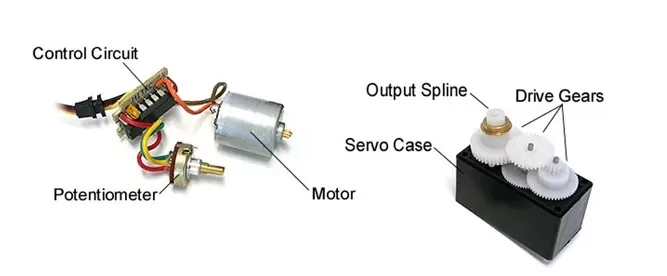
Servo motors are compact, energy-efficient actuators that pack a big punch. They are used in a wide range of applications from hobbyist robots to industrial automation. In this post, we’ll explain how servo motors work and the key components that make them function.
What’s Inside a Servo Motor?
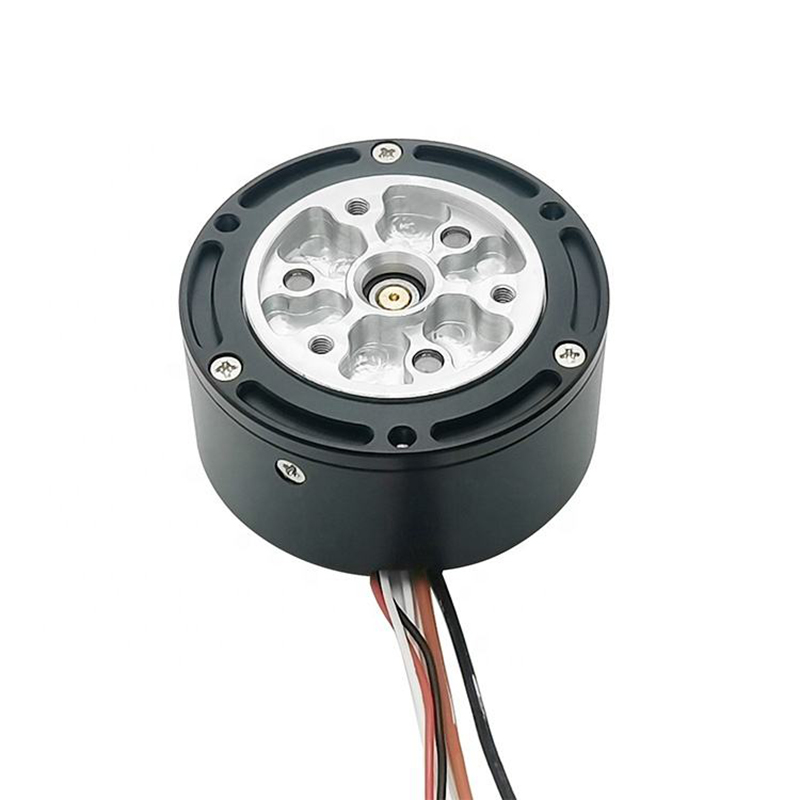
A servo motor contains a small DC motor, potentiometer, control circuitry, and output shaft with a gear. The motor is connected to a potentiometer which can precisely regulate the amount of movement and direction of the output shaft.
When the shaft reaches the target position, power to the motor is cut off. If not at the right position, the motor turns in the appropriate direction until it reaches the target. This type of closed-loop control is called proportional control and makes servos very efficient.
How are Servos Controlled?
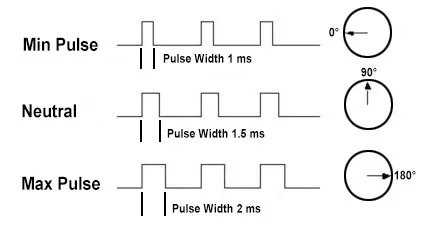
Servos are controlled by sending pulse width modulation (PWM) signals to the control wire. A repeating pulse is sent every 20ms with the pulse width determining the position.
For example, a 1.5ms pulse moves the shaft to 90°, shorter pulses rotate counter-clockwise toward 0°, and longer pulses rotate clockwise toward 180°. If an external force pushes against the servo, it will resist moving to maintain its position.
AC vs DC Servo Motors
Servos come in AC and DC varieties. AC servos can handle larger current surges so are common in industrial applications. DC servos are less expensive but can’t handle large power fluctuations, making them suitable for smaller hobbyist projects.
Continuous rotation servos feature ball bearings on the output shaft to reduce friction. This allows them to spin continuously in either direction making them ideal for powering robots.
Applications of Servo Motors
Some common uses of servo motors include:
- Radio controlled vehicles – For controlling rudders, elevators and other surfaces.
- Robotics – For precise positioning of joints and grippers.
- Manufacturing – Inline tasks requiring high precision and repeatability.
- Food service/pharma – Where frequent high-pressure washdowns require corrosion resistant designs.
Understanding how servos work opens up more possibilities for projects. Whether you’re an engineer, hobbyist, or just curious about electronics – servo motors offer versatile and precise motion control in a small package.